Governance mechanisms for cross-border functional areas (CROSSGOV)
1. 9. 2024 |
— 28. 2. 2026 |
-
Smluvní výzkum:ne
-
Zdroj financování:ESPON EGTC (European Grouping on Territorial Cooperation)
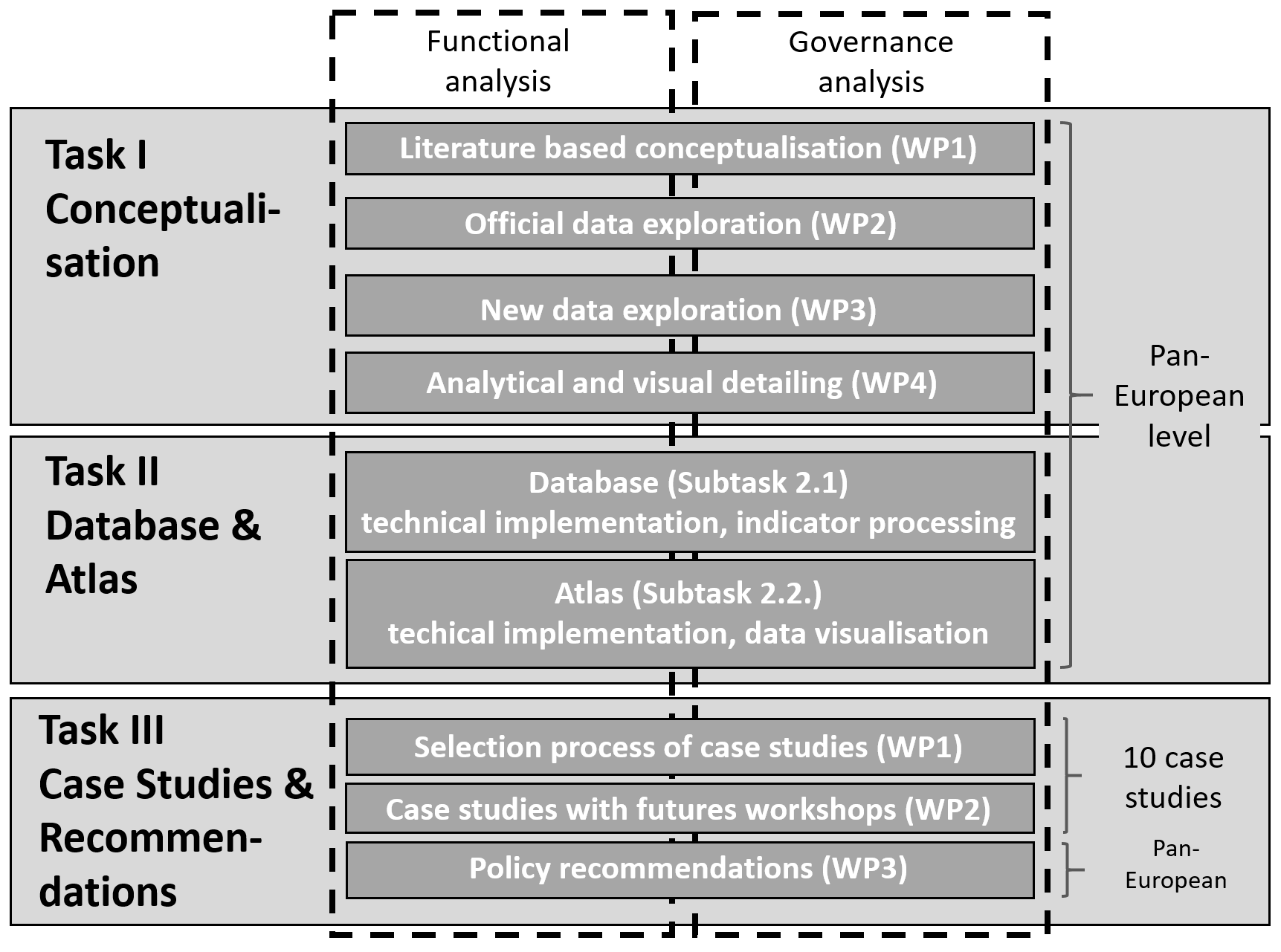
Even if the relevance of cross-border integration is widely recognised, the governance solutions are often incremental, and the analytical knowledge remains limited. Against this background, the CROSSGOV project aims to reach ‘next levels’ of analytical under-standing and to concretise measures for exploiting the potential of governance in border regions. The consortium brings together dif-ferent partners with highly comparative expertise, allowing for a comprehensive reflection, interpre-tation and solution development.
It is amongst the main objectives of the tendering consortium to develop new solutions to existing data limitations. This will be implemented in three ways:
– New data: The current phase of digitalisation comes along with a series of ‘new’ and ‘big’ data that has hardly been used for regional analyses yet. A huge set of new data will be explored with regard to their potential regarding border related analyses.
– New data generation: The tendering consortium brings together complementary partners with cutting-edge competences in the generation of new data (e.g. via web scraping techniques for the housing sector, or big data processing for mobility flows.
– Data combination: The combination of non-harmonised data might not be optimal in the last in-stance, but there are a series of techniques that allow for a certain pragmatism when combing e.g. demographic data that are not dated on the very same day. Regional statistical tools are important in this context (e.g. indexation and interpolation).
Governance of cross-border functional areas is a highly complex analytical object. The tendering consortium will address this field with structured approach that allows for a) comparative analyses, b) atlas based visualisation and c) a solid factual basis enabling improvements in European cross-border governance.
Project structure: